1. Introduction
When we started our halal certification activities in 2010, it was not as easy to obtain halal meat in Japan as it is now, and even if it was available, it was mainly imported frozen products, and most of them did not fit Japan food. Later, with the rise of inbound tourism triggered by the decision to host the Olympic Games, the demand for halal foods and halal certification increased in Japan, and halal foods gradually became known to the general public. Recently, with the spread of online shops, it has become possible to procure halal meat with a single mobile phone and enjoy halal foods from various countries. On the other hand, in the world, “Global Halal Industry” is gaining momentum year by year as an emerging industry. Today, the needs of consumers seeking halal are not limited to food, but are expanding to everything related to daily life, including pharmaceuticals, supplements, cosmetics, clothing, tourism, and finance. Since the halal industry covers everything related to the life of Muslims in general, it can be said that it is an industrial field with a lot of room for growth, such as wedding and funeral ceremonies, education, sporting goods, and matching apps. However, in order to enter the halal industry, it is not essential to acquire halal certification. Regarding entry into the halal industry, we recommend that you carefully gather information in advance, determine whether it is really necessary to acquire halal certification, and proceed with the acquisition of certification. There is no need to obtain certification until halal certification is not required. Bearing in mind that halal certification is only for increasing added value to consumer needs, we hope that you will determine whether halal certification is really necessary and utilize it as your company’s marketing tool.
2. What is Halal Certification?
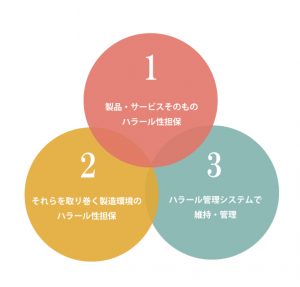
Simply put, halal certification is a mechanism to confirm with objective evidence that “things prohibited by Islam” or “haram” are not included in products and services, and certify them. Our halal certification audits disclose all information about products and services that are subject to certification and confirm that they do not contain “potentially or suspicious haram.” In the case of products, not only the raw materials themselves, but also the manufacturing process of the product and raw materials, the packaging materials used, and the internal management methods are subject to audit. The auditors check them one by one to confirm that the possibility of haram has been eliminated and that halal status has been ensured. Even raw materials that are originally halal may be damaged by touching haram in the manufacturing process. Therefore, it is important not only to ensure the halal nature of the raw materials of products themselves, but also to ensure the halal nature of their manufacturing processes and the surrounding environment.
By managing each of these three import elements, you can ensure that halal certification is operated.
3. What are Halal Certification Standards and Halal Certification Systems?
Halal certification audits are conducted based on the Halal Certification Standards. Although there are several key certification standards used in national certification audits around the world, there is no uniform global certification standard. This is one of the factors that make halal certification difficult to understand. Therefore, in 2019, the Association formulated its own certification standard “JHAS” incorporating the certification standards of major countries, and decided to use it in certification audits. As a result, certified products certified by the Association meet the minimum standards that must be met in each country, and it can be said that the safety and reliability when exporting as halal certified products has increased. Also, like halal certification standards, the halal certification system itself varies from country to country. There are countries where halal certification is carried out directly by government agencies (e.g., Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, etc.), countries where certification bodies accredited and managed by the government (e.g., Australia, etc.), and countries where voluntary organizations do not have government accreditation itself and perform halal certification (Japan, Europe and the United States). In particular, the lack of a way to measure the credibility of halal certification organizations in countries where there is no government accreditation system has become a problem in the world, and an overseas approval/accreditation system for certification organizations was born as one guideline for measuring the credibility of certification organizations.
4. Features of the Association’s Halal Certification
JAKIM was approved as a halal certification organization by the Malaysian government JAKIM in 2012 and by MUIS in Singapore in 2013. Later, in 2016 Japan we became the first halal certification organization in Japan to be accredited by the Gulf States Approval Agency GAC. GAC accreditation is granted only to organizations that conduct halal certification fairly in accordance with international standards, and is considered to be the most reliable accreditation internationally. In addition, we obtained approval from Thai CICOT in 2018, Indonesian MUI in 2019, and Taiwan THIDA in 2020 Turkey HAK and Indonesia BPJPH in 2024. Therefore, as of 2024, the Association’s Halal Certificate is recognized as a valid Halal Certificate in countries such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, the Gulf states, Turkey, Thailand and Taiwan.